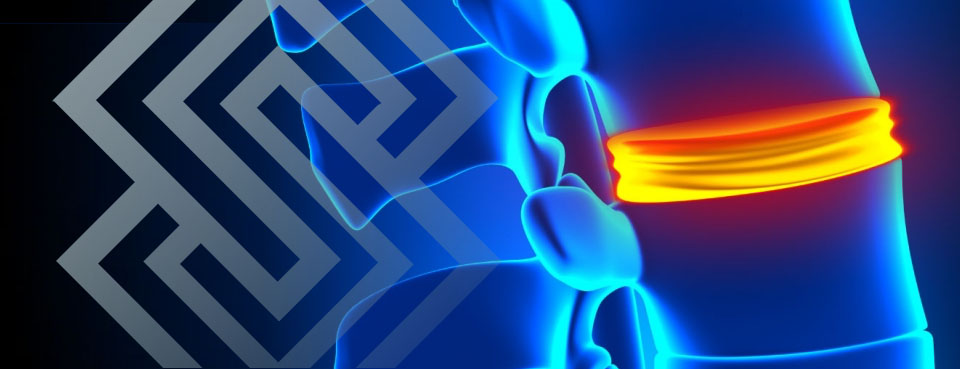
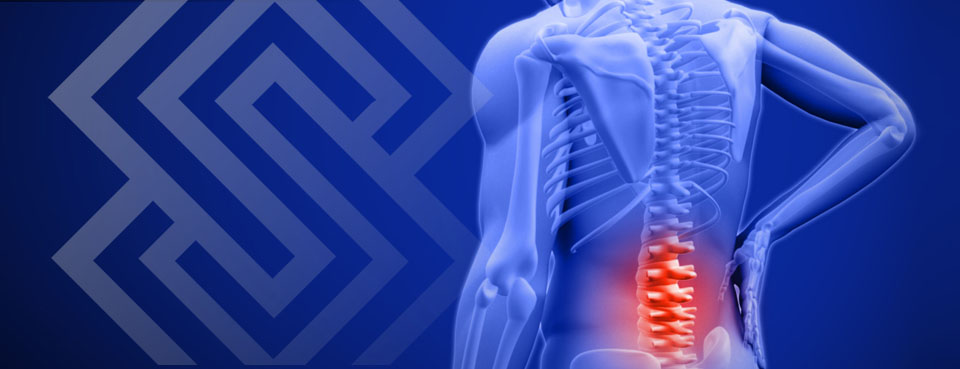
Herniated Disc
Herniated disc is a common condition that can occur anywhere on the spine. It usually occurs on the lower back lumbar areas or on cervical neck regions. Also known as a slipped or ruptured disc, a herniated disc develops when one of the discs between vertebraes moves out of position and compresses adjacent nerves.Herniated discs are typically caused by repetitive movements resulting in injuries or trauma to the spine. Herniated discs can also develop as a result of the normal aging. Genetic factors can also contribute to the development of disc degeneration and herniation. A herniated disc in the lower back can heal within 6 months without surgical intervention, as the size of herniation recedes with time. Surgery may be needed if medication, physical therapy and other treatments fail to resolve the herniation.
Herniated Disc Causes
Spinal discs dehydrate from age 30 and the loss of fluid progresses slowly during our lifetime. As the discs lose water, microscopic cracks or tears can form on the outer annulus fibrosus, causing it to become hard and prone to damage, tears and injury. Common causes of herniated disc include:• Wear and tear from age.
• Repetitive movements performed during work and/or sports activities that put pressure on the spine.
• Incorrect lifting of heavy objects.
• High-impact trauma cause injury to the disc in the form of ruptures, bulges or tears.
• Obesity.
• Genetic predispositions.
/h5>Herniated Disc Symptoms Pain from a herniated disc can vary, depending on the area of the spine effected and extent of a spinal disc injury. If an injury is minor, little to no pain may be experienced. A ruptured disc can also cause severe pain if damage to the disc is severe. Pain may emanate to extremities following a specific nerve root path if significant nerve compression occurs. Sciatica can be caused by a herniated disc in the lower back and radiation down one leg. Herniated discs can present with a wide range of symptoms including:
• Dull aching to severe pain.
• Numb, tingling or burning sensations.
• Muscle weakness and spasms with abnormal reflexive muscle reactions.
If you experience a loss of bladder control, seek emergency medical care immediately as this may mean a bulging disc is compressing the cauda equina nerves and can be a life threatening condition.
Notice:
This advertisement has been provided for informational purposes only and should not be used as a substitute for medical treatment or an actual diagnosis. If you are experiencing pain that may be associated with back or neck disorders you should seek the care of a doctor as soon as possible or immediately if your symptoms are accompanied by incontinence / loss of bladder or bowel control, as these may be signs of life threatening condition.